Proper warm-up, conditioning exercises can help prevent youth sports injuries
Proper warm-up, conditioning exercises can help prevent youth sports injuries
Home / Knee Surgeon Chicago Illinois / Prepatellar Bursitis
A bursa functions like a water balloon to reduce friction and wear of the soft tissues against bone. The prepatellar bursa is a bursa between the patella (kneecap) and the overlying skin. This bursa allows the skin to glide easily and without friction over the patella. Prepatellar bursitis is characterized by inflammation and pain of this bursa.
Initial treatment consists of medication and ice to relieve the pain, stretching and strengthening exercises (particularly the quadriceps and hamstring muscles), and modification of the activity that initially caused the problem. These all can be carried out at home, although referral to a physical therapist or athletic trainer for further evaluation and treatment may be helpful. For those on their knees often or for those at risk of falling and landing on the knees, knee pads should be worn to protect the bursa while the inflammation settles down. An elastic bandage may be used to help reduce swelling. If symptoms persist or recur, withdrawing fluid from the bursa, with or without injection or cortisone, may be needed. Bursae that persist despite conservative treatment, that recur, or that are infected may require surgical excision (removal).
Learn More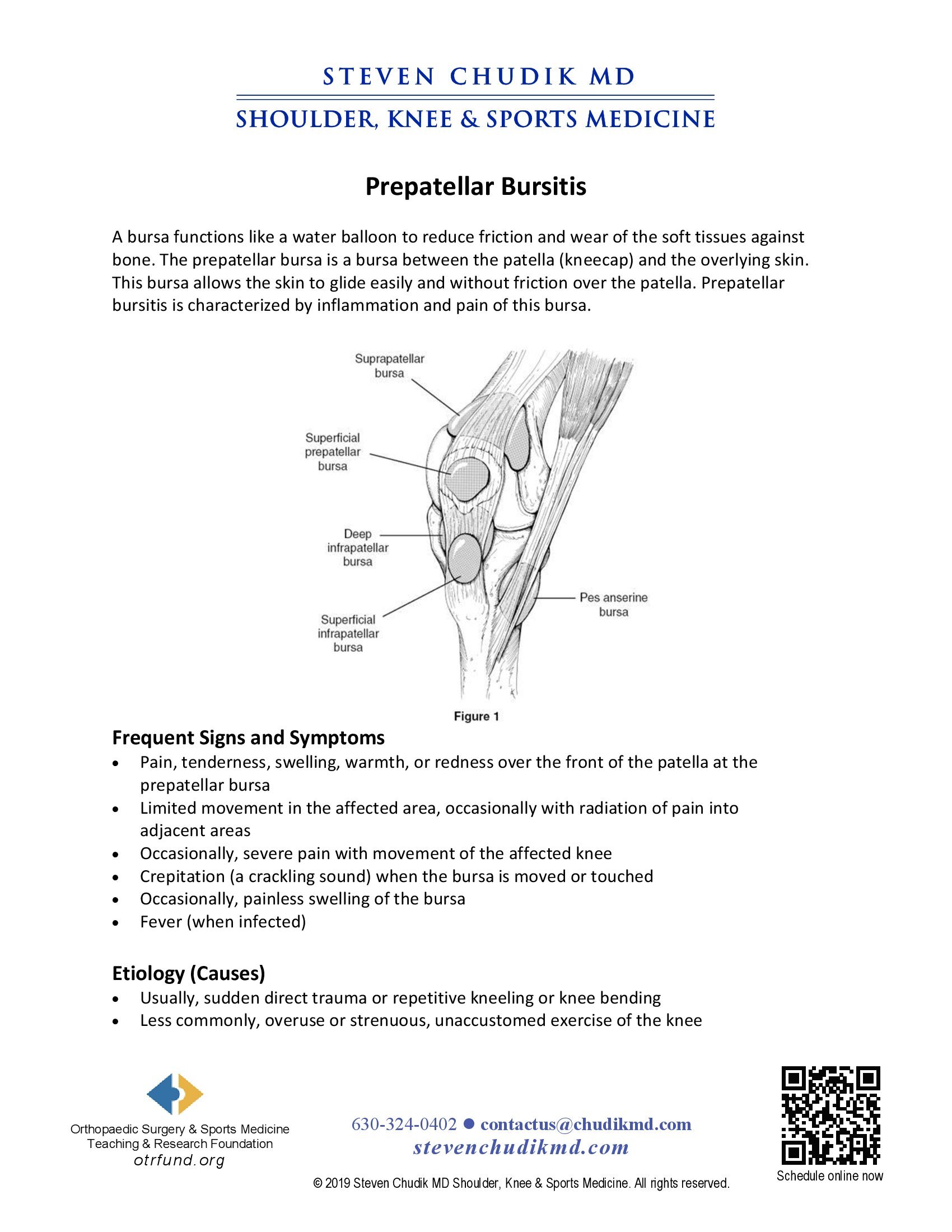
 Second shoulder work injury jeopardized Kucera’s job, bow hunting pastime
Second shoulder work injury jeopardized Kucera’s job, bow hunting pastime
Dr Steven Chudik founded OTRF in 2007 to keep people active and healthy through unbiased education and research. Click to learn about OTRF’s free programs, educational opportunities and ways to participate with the nonprofit foundation.
1010 Executive Ct, Suite 250
Westmont, Illinois 60559
Phone: 630-324-0402
Fax: 630-920-2382
(New Patients)
550 W Ogden Ave
Hinsdale, IL 60521
Phone: 630-323-6116
Fax: 630-920-2382
4700 Gilbert Ave, Suite 51
Western Springs, Illinois 60558
Phone: 630-324-0402
Fax: 630-920-2382

© 2025 © 2019 Copyright Steven Chudik MD, All Rights Reserved.